Understanding Professional Heat Pumps with Benefits and Installation Insights
January 20, 2026

In today’s evolving energy landscape, homeowners and businesses alike are seeking efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective solutions to maintain comfortable indoor environments. Heat pumps have emerged as a leading technology that addresses these needs by providing both heating and cooling in a single, energy-efficient system. Unlike traditional HVAC systems that rely on separate units for heating and cooling, modern heat pumps transfer heat between indoor and outdoor spaces, making them versatile and environmentally friendly. As energy costs rise and environmental awareness grows, understanding the advantages and functionality of professional heat pumps has become increasingly relevant.
Choosing the right heat pump involves more than selecting a high-efficiency model. Proper installation, system sizing, and maintenance play critical roles in maximizing performance, extending lifespan, and ensuring safety. Professional guidance ensures that your system operates optimally while complying with local regulations and industry standards. This blog delves into the benefits of heat pumps, essential installation insights, and practical tips to make an informed decision. By exploring real-world scenarios, challenges, and best practices, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of why professional heat pump solutions are not only a practical choice but also a long-term investment in comfort, energy efficiency, and home value.
1. How Heat Pumps Work: Core Functionality
Understanding the Basic Principle
At their core, heat pumps operate on the principle of heat transfer. Unlike conventional systems that generate heat through combustion or resistive elements, heat pumps extract thermal energy from one environment and transfer it to another. In heating mode, they pull heat from outdoor air, the ground, or water and release it indoors. In cooling mode, this process is reversed, removing heat from indoor air and expelling it outside.
Types of Heat Pumps
There are several types of heat pumps, each suited for specific climates and applications:
- Air-Source Heat Pumps: Most common, extracting heat from ambient air. Modern versions work efficiently even in colder climates.
- Ground-Source (Geothermal) Heat Pumps: Utilize underground temperatures to provide consistent heating and cooling, offering higher efficiency but requiring higher initial investment.
- Water-Source Heat Pumps: Draw heat from nearby water sources, ideal for commercial or industrial settings with access to lakes, ponds, or wells.
Real-World Example
Consider a mid-sized home in a region with cold winters and hot summers. An air-source heat pump can maintain indoor comfort year-round while reducing energy consumption compared to separate heating and cooling systems. By transferring heat instead of generating it, homeowners can save significantly on utility bills.
2. Key Benefits of Professional Heat Pumps
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
One of the most compelling advantages of heat pumps is their energy efficiency. By transferring heat rather than generating it, they consume less electricity than traditional electric heaters. In practical terms, this means:
- Reduced Energy Bills: Homeowners often see 30–50% lower heating costs.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Reduced reliance on fossil fuels aligns with sustainability goals.
Versatility and Year-Round Comfort
Heat pumps provide both heating and cooling in a single system, eliminating the need for separate units. This dual functionality simplifies maintenance and reduces equipment costs. Homeowners can enjoy:
- Consistent Indoor Climate: Even distribution of heat and cooling throughout the home.
- Smart Integration: Modern heat pumps often integrate with smart thermostats and home automation systems for optimal control.
Reliability and Longevity
Professional installation ensures that heat pumps operate reliably over many years. Proper sizing, refrigerant charging, and ductwork design prevent common issues like uneven heating or compressor strain, extending system life.
Environmental Benefits
As global energy efficiency standards tighten, heat pumps provide an eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuel-based heating. Using electricity, ideally from renewable sources, further minimizes greenhouse gas emissions.
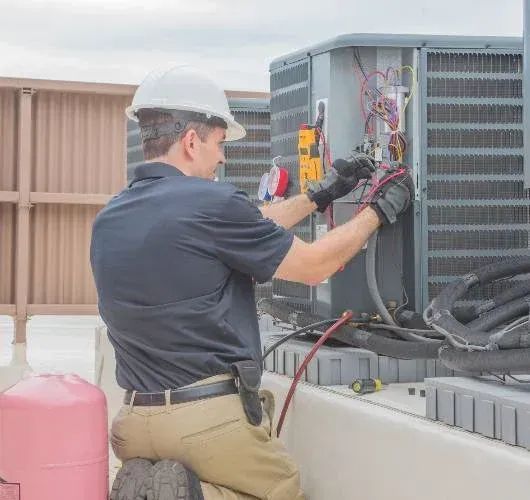
3. Professional Installation Insights
Importance of Expert Installation
Correct installation is crucial to achieving the full benefits of a heat pump. Improper installation can lead to reduced efficiency, frequent repairs, and premature system failure. Professional technicians follow industry best practices to:
- Accurately calculate heating and cooling loads based on building size and insulation.
- Correctly size the heat pump to avoid overworking the system.
- Install ductwork, refrigerant lines, and controls according to manufacturer specifications.
Site Assessment and Planning
Before installation, professionals conduct a thorough site assessment. This includes evaluating:
- Insulation and Air Sealing: Poor insulation can reduce efficiency and increase energy costs.
- Existing HVAC Infrastructure: Integrating with existing ductwork or designing a new layout for optimal airflow.
- Climate Considerations: Air-source heat pumps perform differently depending on local temperature patterns; cold-climate models are often necessary for northern regions.
Installation Process
The professional installation process generally includes:
- System Placement: Positioning outdoor and indoor units for optimal airflow and maintenance access.
- Refrigerant Handling: Charging the system with the correct refrigerant amount and type.
- Electrical Integration: Connecting the system safely to the home’s electrical network.
- Testing and Calibration: Ensuring the system operates efficiently and safely, with proper airflow, pressure, and thermostat settings.
Real-World Scenario
A family in Missouri upgraded to a professional heat pump system after repeated breakdowns of their old furnace and air conditioner. The installer assessed the home, recommended a properly sized air-source heat pump, and completed the installation with minimal disruption. Post-installation, the family reported balanced temperatures throughout the house and significant energy savings.
4. Common Challenges and How to Address Them
Climate-Related Efficiency Drops
In extremely cold conditions, standard air-source heat pumps may struggle to extract sufficient heat from the outside air. Solutions include:
- Installing cold-climate heat pumps with enhanced compressors.
- Using supplemental heating options such as electric resistance strips or hybrid systems.
System Sizing Errors
Undersized systems cannot adequately heat or cool a space, while oversized units cycle frequently, reducing efficiency. Addressing this requires:
- Load Calculations: Conducted by a professional using manual J or equivalent methods.
- Custom Recommendations: Ensuring the heat pump meets the unique demands of the property.
Maintenance Requirements
Heat pumps require regular maintenance for optimal performance. Professionals recommend:
- Annual Inspections: Checking refrigerant levels, electrical connections, and airflow.
- Filter Replacement: Clean or replace filters every 1–3 months to maintain air quality and efficiency.
- System Cleaning: Periodic cleaning of coils and ducts to prevent blockages and wear.
Noise and Space Considerations
While generally quiet, improper installation can cause vibrations or noise. Placement of outdoor units, proper mounting, and use of vibration dampers can minimize these issues.
5. Best Practices for Maximizing Heat Pump Performance
Optimal Thermostat Management
Using programmable or smart thermostats allows homeowners to set energy-saving schedules, reducing unnecessary heating or cooling when spaces are unoccupied.
Energy-Saving Habits
Simple behavioral adjustments can enhance system efficiency:
- Closing blinds during summer to reduce cooling loads.
- Sealing windows and doors to prevent heat loss in winter.
- Regularly inspecting and maintaining ductwork for leaks.
Leveraging Rebates and Incentives
Many regions offer financial incentives for heat pump installation due to their energy efficiency. Professionals can guide homeowners through:
- Federal Tax Credits: Incentives for energy-efficient home upgrades.
- Utility Rebates: Local energy providers may offer rebates for high-efficiency units.
Integration with Renewable Energy
Pairing heat pumps with solar panels can further reduce electricity costs and environmental impact, creating a sustainable home heating and cooling solution.
6. Choosing the Right Heat Pump and Installer
Evaluating System Options
When selecting a heat pump, consider:
- Efficiency Ratings: SEER (cooling) and HSPF (heating) ratings indicate performance.
- Capacity: Match system capacity to home or building size.
- Features: Variable-speed compressors, smart connectivity, and quiet operation.
Selecting a Professional Installer
Hiring a certified, experienced installer ensures system longevity and efficiency. Look for:
- Licensing and Certifications: Verified credentials from recognized HVAC organizations.
- Experience and References: Proven track record with heat pump installations.
- Warranty and Support: Comprehensive warranties and maintenance services for peace of mind.
Real-World Example
A small business in Edwards, Missouri, needed a climate control upgrade. The professional installer recommended a variable-speed heat pump system tailored to the building’s layout. Post-installation, the business experienced reduced energy bills, uniform indoor temperatures, and a quieter environment, highlighting the benefits of choosing a qualified professional.
Innovative Features of Modern Heat Pumps
Advanced Refrigerant Technology
Modern heat pumps use eco-friendly refrigerants that reduce environmental impact while enhancing efficiency and reliability.
Smart Home Integration
Integration with home automation systems allows users to control temperature remotely, monitor energy usage, and receive maintenance alerts, improving convenience and performance.
Zoning Capabilities
Advanced heat pumps can create zones within a home or building, allowing different areas to be heated or cooled independently. This ensures comfort and reduces energy waste.
Longevity Enhancements
Features like variable-speed compressors and corrosion-resistant coils extend the operational life of heat pumps, making them a durable and sustainable investment.
Maximizing Comfort Through Proper Heat Pump Use
Professional heat pumps offer a transformative solution for modern heating and cooling needs. By efficiently transferring heat rather than generating it, these systems deliver year-round comfort, significant energy savings, and environmental benefits. Proper sizing, installation, and maintenance are critical to maximizing performance, preventing system issues, and ensuring long-term reliability. Understanding the different types of heat pumps, their operational principles, and integration options allows homeowners and businesses to make informed decisions tailored to their unique climate and space requirements.
For those considering a
professional heat pump installation
in Edwards, Missouri, ProTech Heat-Cool LLC
stands as a trusted authority with 30
years of experience in delivering reliable, efficient, and expertly installed HVAC solutions. Our team provides comprehensive assessments, precision installations, and ongoing maintenance services, ensuring optimal system performance and energy efficiency. With a commitment to quality, transparency, and customer satisfaction, ProTech Heat-Cool LLC
is the go-to choice for families and businesses seeking dependable heating and cooling solutions that combine comfort, savings, and sustainability.